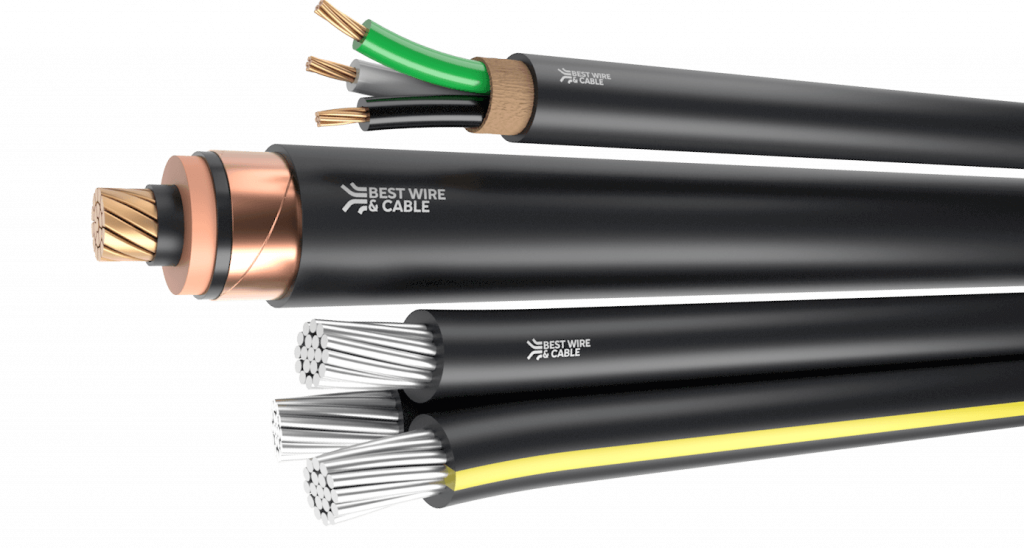
LSZH Cables: Safety, Composition & Why They’re Becoming Essential

When it comes to wiring systems, fire and smoke are the real threats—not just flames. Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH or LSHF or LS0H) compounds are emerging as critical materials for cable insulation and jacketing. They limit toxic emissions, improve safety, and are increasingly mandated by building codes. Let’s dive into what LSZH is made of, its purpose, and how markets are responding — with fresh data to illustrate the trend.
What LSZH Means: Composition & Fire Safety
LSZH compounds are specially formulated materials used for cable insulation and outer jackets. They differ significantly from traditional PVC or other halogenated materials in several ways:
-
Halogen-free: LSZH compounds do not contain chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine or similar halogens.
-
Smoke suppression: When they burn, they emit very low smoke compared to PVC (which generates dense black smoke).
-
Non-toxic emissions: Traditional PVC can release hydrogen chloride (HCl) in large amounts when burned; LSZH materials emit minimal or no halide gas. In lab tests, PVC might release ~28% by weight of HCl under fire; LSZH is often ≤ 0.5%. tstcables.com
-
Materials used: LSZH compounds are often based on polymers like polyethylene (PE), ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). To make them flame retardant, inorganic fillers such as aluminum hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide are added. These fillers help absorb heat (endothermic reaction) and release water vapor.
These properties make LSZH cables safer in enclosed and densely occupied spaces (airports, tunnels, hospitals, high-rise buildings). Reduced toxic gas + lower smoke = better visibility for evacuation and less harm to human health and sensitive electronics.
Why the Industry Needs LSZH: Purpose & Use Cases
LSZH is no longer just “nice to have.” It’s increasingly required. Here’s why and where it’s making a difference:
-
Fire safety & regulations
Many building codes now require LSZH-rated cables in public areas, transportation systems, underground tunnels, data centers, and medical facilities. For example, after the King’s Cross fire in London (1987), regulations banned PVC cables in certain underground installations. The Big Red Guide -
Protecting health & equipment
Smoke inhalation causes over 80% of fire-related fatalities because of toxic gases in smoke. LSZH helps reduce that risk by limiting hazardous combustion by-products. Ctube Official+1 -
Reducing property damage & liability
Less corrosive smoke means less damage to electronics, metals, and finishes during a fire. Also, insurance premiums and legal liabilities tend to be lower for structures using safer cable materials. -
Performance & durability
Low Smoke, Halogen-Free compounds are increasingly engineered for mechanical strength, UV and thermal resistance, and rigid flame ratings—making them more than just “safe” but also robust in harsh environmental conditions.
Market Trends & Statistics
The adoption of Low Smoke, Halogen-Free cables is accelerating globally. Here are current market and growth figures:
-
The global LSZH cables market is growing at a CAGR of around 7-8% from 2023 through the early 2030s. WiseGuy Reports+2Dataintelo+2
-
As of 2023, the LSZH cables market was valued at about USD $13.72 billion, and it’s forecast to reach approximately USD $30.85 billion by 2032. WiseGuy Reports
-
The LSZH flame retardant optical cables segment had a dominant share in telecommunications (~40%) in 2023. Verified Market Reports
-
Regionally, Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market, driven by infrastructure growth, urbanization, and stricter safety regulations. Its CAGR is predicted at ~ 8-8.5% from 2025-2033. Growth Market Reports+1
-
Europe remains a strong market too, especially because strict fire safety building codes. Europe’s Low Smoke, Halogen-Free cable market size was about USD $1.48 billion in 2024. Growth Market Reports
-
In control and power cable segments, LSZH is increasingly specified: up to 50% share in the power cable jacket compounds market in some reports. Verified Market Reports
Challenges & Considerations
While Low Smoke, Halogen-Free cables offer many advantages, there are trade-offs:
-
Upfront cost: LSZH materials often cost more per foot/meter than standard PVC (15-30% more depending on specifications).
-
Mechanical properties: Some LSZH compounds are less flexible than PVC, harder to process or install in tight or highly bending installations (though newer formulas are improving this).
-
Availability: In some regions, non-LSZH cables are still dominant, due to cost constraints or less strict code enforcement.
What’s Ahead: Innovations & Future Outlook
-
Manufacturers are introducing LSZH cables with broader temperature ranges (e.g. -40°C to +125°C) to handle extreme climates and renewable energy installations. Market Growth Reports
-
Hybrid cables combining signal + power with Low Smoke, Halogen-Free jackets are appearing for smart lighting, building automation, and EV-charging infrastructure. These reduce wiring volume and simplify installations. Market Growth Reports
-
Demand from green building certifications, smart cities, transportation infrastructure, and EV charging networks are pushing LSZH adoption further. Codes will likely tighten.
Closing Insights
LSZH / LSHF / LS0H compounds are no longer optional in many high-risk or enclosed environments. With their low smoke output, reduced toxic emissions, and increasingly strong performance, LSZH cables are becoming standard in many sectors. Market data confirms strong growth—and it’s driven by safety, regulation, and performance.
If you’re designing or building systems for hospitals, data centers, transit, or sustainable infrastructure, specifying Low Smoke, Halogen-Free cables isn’t just safer—it’s increasingly the expectation.
Discover the benefits of LSZH cables—check us out today for safer, smarter solutions!